Content:
Stellar is one of the widely known cryptoprojects, this is facilitated by a long history, high capitalization, the prominence of the founders, and the presence of partnerships with large companies. It is worth noting that despite the average high recognizability of the project, the bright news occasions associated with it do not arise too often. For a while there was a little criticism in the project’s community of the team for not paying proper attention to marketing. By now the situation has improved somewhat in a positive direction, for example, the team has plans for conferences. Despite the lack of active marketing, big occasions for the crypto environment such as the launch of a joint project with IBM, for example, could not go unnoticed. Most publications have published articles related to Stellar.
Popularity of social accounts:
Applicability
According to stellar.expert explorer (at the time of writing) there are a total of 6’177’814 accounts registered online, with 45’195 of them active during the same day. Also during the last day 258’953 payment transactions were processed.
Graph of the total number of accounts and the number of active accounts (stellar.expert):
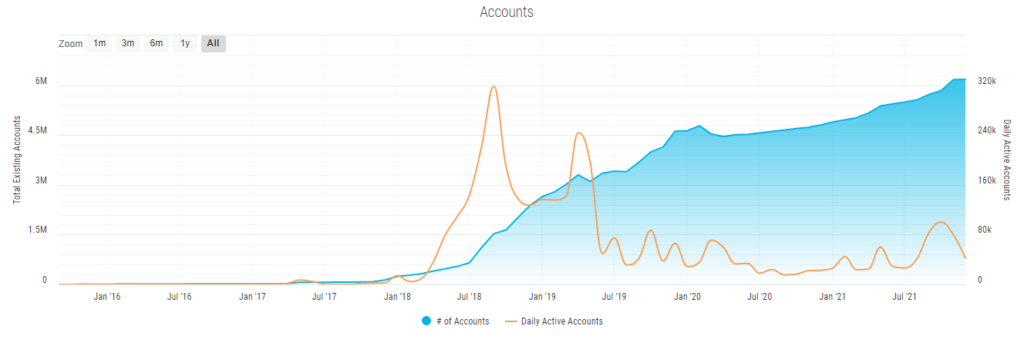
As can be seen from the graph, despite the increase in the total number of accounts, the number of active accounts is decreasing.
In total, 111 public nodes were launched in the Stellar network, which is quite small for a project with such a long history. Perhaps, the small number of nodes is due to the fact that the SCP algorithm does not provide any incentive mechanisms for the owners of the nodes involved in providing consensus.
As of December 3, 2021, the total number of XLM tokens exceeds 50 billion, with about 24.63 issued into circulation (not held by the fund). The distribution of XLM is highly centralized, which forms certain risks for the project.
Projects powered by Stellar
Quite a few companies use the Stellar protocol to perform fast cross-border transfers in their business. Among the launched projects worth mentioning are:
- Deloitte, one of the largest financial advisory firms in the world, which launched a prototype Deloitte Digital Bank solution based on Stellar for international instant payments. As a result, transaction costs have been reduced by 40% and transaction speeds have been reduced to 5 seconds..,
- Tempo uses the Stellar network to reduce costs and increase transparency of money transfers. The company has a network of 190’000 locations in 120 countries, through which customers can make cross-border payments for utilities, phone, health insurance, etc.
- As a licensed mobile operator, Parkway uses the Stellar network to connect Nigeria’s 5 largest telecommunications companies, allowing customers of different services to send money to each other. Parkway develops financial technology for 3’000 customers across Africa, including Ecobank, Wema Bank and Diamond Bank. Their end-to-end financial solutions are used in 30 countries in sectors such as healthcare, education and energy.
- In October 2017, it was announced that IBM was going to use Stellar for the cross-border payments industry. The project is supported by major companies such as National Australia Bank, TD Bank, Wizdraw (HK) of WorldCom Finance and the UN and Swift’s Advancement of Pacific Financial Infrastructure for Inclusion (APFII), a division of Polynesian payment system KlickEx. The new payment system is already built into IBM’s Financial Transaction Manager.
- In 2018, IBM announced the launch of a project for the cross-border payments sphere based on the Stellar protocol, Blockchain World Wire, to which any financial institutions can connect.
- India’s largest private bank, ICICI Bank, uses Stellar technology to execute international transfers.
- SatoshiPay, a micropayment solution, started using Stellar technology due to its low transaction costs.
Trust Index
The Stellar project was launched by Jed McCaleb after he left the Ripple project, where he was also a founder. The reason for Jed’s abrupt departure from Ripple was that the project was too centralized and non-transparent.
A non-profit foundation was launched to manage Stellar, which is not supposed to make any profit from the project’s activities. Despite the initial goal of forming a truly decentralized project, Stellar also had aspects of centralization, particularly related to token distribution.
As of December 3, 2021, the Stellar Development Foundation holds just over 50% of the total number of tokens. That said, it’s worth noting that Jed McCaleb is also the founder of Interstellar, a for-profit company that aims to expand the ecosystem of services and partnerships around Stellar. The combination of having a large number of tokens in the hands of the foundation with the presence of a commercial organization with close management raises concerns among many users.
It’s also worth noting that Jed McCaleb is the founder of the Mt.Gox exchange, which has an infamous story with the largest hack and theft of bitcoins in history. Some users associate Jed with the tarnished reputation of this project, but it should be noted that he left it much earlier than the designated events. But in general, having two examples of Jed’s rather abrupt departure from his projects (Ripple and Mt.Gox) is also worrying for users, as it raises fears that one day a similar situation could occur in Stellar.
The premade of XLM tokens, combined with the high centralization of funds, forms the risks of a drop in value if a large number of assets go into circulation. Because of this, many cryptocurrency investors refrain from adding Stellar to their portfolios. In addition, Stellar had an inflationary mechanism (1%), through which additional XLM tokens are added to the circulation, which are accrued to the address that received more than a fixed number of user votes. With this mechanism, firstly, centralized pools that agitate users to vote for their pool with a promise to distribute tokens to voters later can gain an advantage.
Second, the weight of the vote depends on the number of XLM tokens in the voter’s account, and XLM distribution is highly centralized. Thus, a potential risk is formed that some users may constantly shift votes in their favor, getting extra XLMs into their “big” wallets. But as of version 12 of the protocol, Stellar has eliminated the inflationary mechanism, which has had a positive effect on the price of the cryptocurrency.
It is also worth noting that the network lacks mechanisms for rewarding validator nodes, which may have a negative impact on increasing decentralization of the Stellar network, as users have no clear motivation to run a node.
In May 2019, the Stellar network failed to validate transactions for several hours, confirming concerns about the risks in the SCP consensus mechanism used and the centralization of the network. Due to the shutdown of some Stellar Development Foundation (SDF) nodes, the network was unable to reach consensus and confirm transactions. It’s worth noting that no one has lost their funds in the process.
Also in April 2021 there was a shutdown of more than half of the validators, which suspended the network of Stellar for 10 hours. This caused the price of the cryptocurrency to fall by about 20% during the day. SDF engineers later managed to fix the situation, but the reason for the outage remains unknown.
Despite the presence of reaction from the team and the desire to minimize the problem, today there is a risk of a repeat of the network shutdown. It is worth noting that in the event of a node outage, Stellar’s algorithm works differently than most blockchains in the sense that there is no fork in the network, it just stops working.
Some believe that especially for financial institutions this approach is more correct because it reduces the chances of losing money. But in any case, the fact that any network depends on a few nodes signals its instability. And this issue is even more acute for the system, which is declared decentralized.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Stellar team created and is developing a protocol that allows users to make fast, cheap cross-border payments, including in assets tied to familiar currencies. The team’s solution has found application in end-users and crypto projects as well as in the real sector.
The advantages of the project include:
- Extensive opportunities for creating and pegging assets.
- Availability of a decentralized asset exchange.
- A competent team.
- The launch of large projects based on the Stellar protocol.
- Wide popularity and a large user base.
Major disadvantages:
- Centralization of XLM distribution and keeping more than 50% of tokens in the Stellar fund.
- Lack of rewards for validators.
- Potential risks of the SCP consensus algorithm, confirmed by the network shutdown in May 2019 and April 2021.
